By Abby Krause, DNR Urban Forestry Coordinator; Abigail.Krause@wisconsin.gov or 608-556-5690
 Tree City USA is an annual recognition program presented by the Arbor Day Foundation that allows communities to publicly demonstrate their continued commitment to the care of their local urban forest. Returning Tree City USA communities are also eligible to apply for Growth Awards. These awards recognize community forestry programs that go above and beyond the four core tenets of Tree City USA.
Tree City USA is an annual recognition program presented by the Arbor Day Foundation that allows communities to publicly demonstrate their continued commitment to the care of their local urban forest. Returning Tree City USA communities are also eligible to apply for Growth Awards. These awards recognize community forestry programs that go above and beyond the four core tenets of Tree City USA.
Wisconsin has consistently proven to be a national leader in the stewardship of the forests outside our front doors all across the state. In 2023, we saw participation from Milwaukee, our state’s most populous city, down to Ephraim, a village of only a few hundred residents. We ranked third nationally in both programs with 194 Tree City USA communities and 26 Growth Awards. Only Ohio and Illinois ranked higher. Continue reading “Tree City USA: Wisconsin Can Take The Lead In Growth Awards Earned With Your Help”
 Do you remember when you were in fourth grade? Did you receive a tree seedling to plant for Arbor Day?
Do you remember when you were in fourth grade? Did you receive a tree seedling to plant for Arbor Day? The
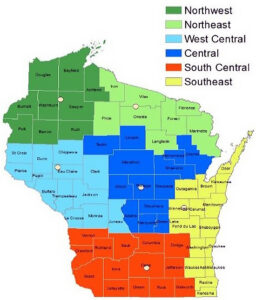
The  Tree City USA Interactive Map
Tree City USA Interactive Map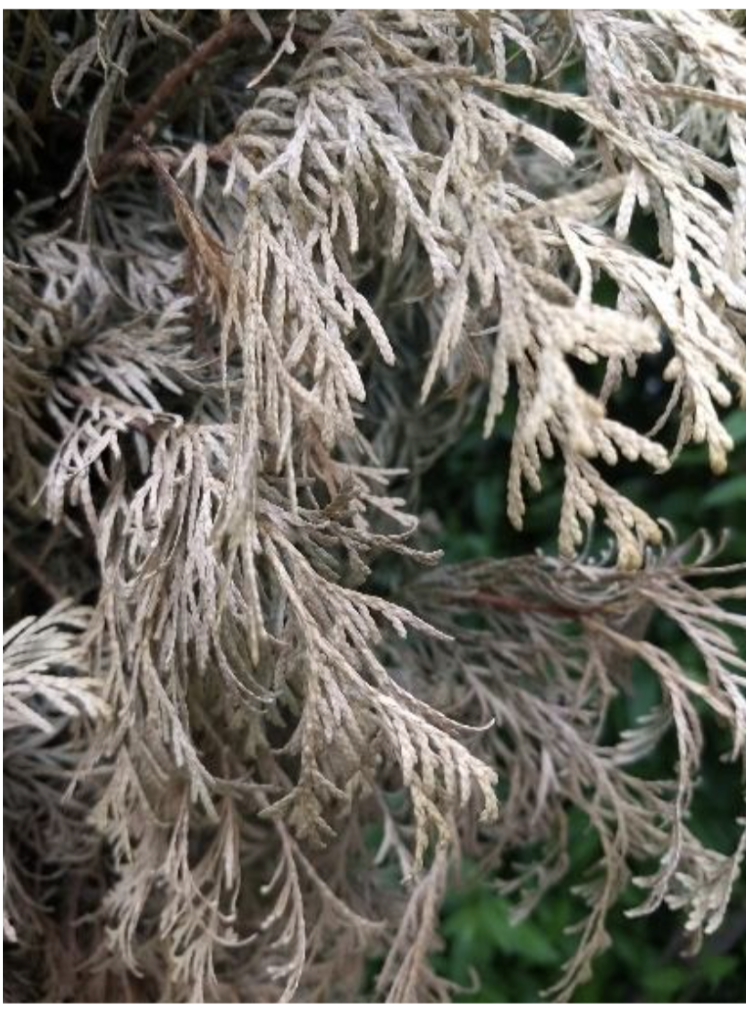 ‘Winter burn’ refers to a type of damage to evergreen foliage that typically occurs over winter. Common symptoms are browning and dying from the tips of the foliage inward. Several factors cause winter burn on evergreens, including winter ‘thaws’ while the ground is frozen, dry soil in autumn, a long period of very cold temperatures, winter sun on evergreen foliage or drying winter winds, poor siting of susceptible plants, recent planting/transplanting and the individual plant’s susceptibility. Frequently affected plants include yews, junipers, boxwood, arborvitae, rhododendrons, dwarf Alberta spruce and hemlock.
‘Winter burn’ refers to a type of damage to evergreen foliage that typically occurs over winter. Common symptoms are browning and dying from the tips of the foliage inward. Several factors cause winter burn on evergreens, including winter ‘thaws’ while the ground is frozen, dry soil in autumn, a long period of very cold temperatures, winter sun on evergreen foliage or drying winter winds, poor siting of susceptible plants, recent planting/transplanting and the individual plant’s susceptibility. Frequently affected plants include yews, junipers, boxwood, arborvitae, rhododendrons, dwarf Alberta spruce and hemlock.