By Olivia Witthun, DNR Urban Forestry Coordinator in Plymouth, olivia.witthun@wisconsin.gov or 414-750-8744
Laura Buntrock, DNR Urban Forestry Partnership and Policy Specialist in Rhinelander, laura.buntrock@wisconsin.gov or 608-294-0253
Dan Buckler, DNR Urban Forest Assessment Specialist in Madison, daniel.buckler@wisconsin.gov or 608-445-4578
Ram Dahal, DNR Forest Economist in Madison, ram.dahal@wisconsin.gov or 715-225-3892
We know that urban forests are a vital component of our economy and environment, making significant financial contributions to local, state and national economies, as well as providing critical ecosystem services. But until recently, the economic contribution of urban forestry has typically been aggregated into the broader green industry.
Background On The Study
In the Urban Forestry Economic Study, a ground-breaking study led by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources and funded through a U.S. Department of Agriculture Landscape Scale Restoration grant, a comprehensive analysis of the economic contributions of urban and community forestry was completed across the Northeast-Midwest region, which includes 20 states and Washington, D.C. (Figure 1). This analysis includes economic impact numbers, employment numbers, industry outlook and a resource valuation.
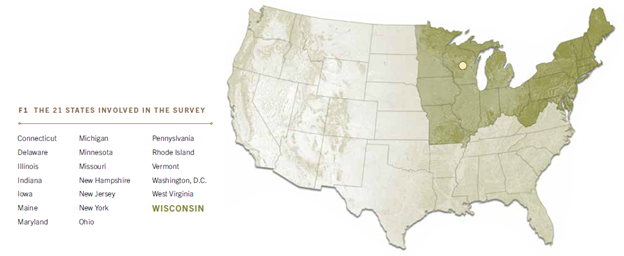
Figure 1. Map depicting the 21 states involved in the survey.
Continue reading “Urban Forestry Economic Analysis In Wisconsin” →