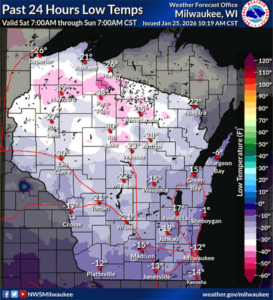
Cold temperatures across the state of Wisconsin on Jan. 25, 2026. / Graphic Credit: National Weather Service
By River Mathieu, DNR Forest Health Specialist, Fitchburg
River.Mathieu@wisconsin.gov or 608-772-2758
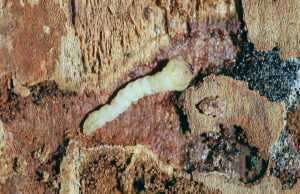
Wisconsin experienced a polar vortex in late January 2026, and temperatures got chilly throughout the state, even reaching close to -40⁰ F in some places! Although it has warmed up, the cold weather is still fresh in everyone’s minds, leaving insect and forest lovers alike wondering how insects survive temperatures that cold.
The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Forest Health staff has received several questions over the past month about how insects survive cold weather in winter and whether the January temperatures were cold enough to kill insect pests.