By Paul Cigan, DNR Forest Health Specialist, Hayward;
https://dnr.wisconsin.gov/topic/foresthealth/staff, 715-416-4920
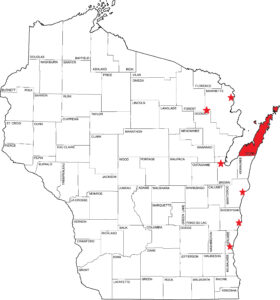
This winter, the spread and impact of emerald ash borer (EAB) have been confirmed in several new northern townships in previously invaded counties.
These include Marengo (Ashland County); Gordon, Hawthorne and Oakland (Douglas County); Cadott and Colburn (Chippewa County) and Balsam Lake and St. Croix Falls (in Polk County).
Continue reading “Emerald Ash Borer Spreads Through The North”