By Todd Lanigan, forest health specialist, Eau Claire. Todd.Lanigan@wisconsin.gov; 715-210-0150
Heterobasidion root disease (HRD), formerly known as annosum root rot, was recently found in Monroe County for the first time in the town of Little Falls. With this detection, HRD is now known to occur in 28 Wisconsin counties.
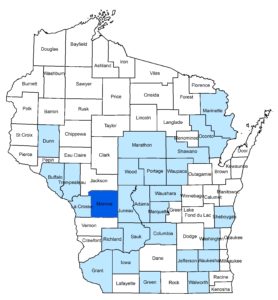
HRD distribution map. Counties where HRD is present are shown in blue with most recently confirmed county shown in dark blue.
Fruiting bodies of the pathogen, Heterobasidion irregulare, were found on dead overstory red pine and both live and dead white pine saplings in the Big Creek Fishery Area. The 20-acre stand was a red pine plantation established in 1958 and last thinned in 2012. Wood samples were collected to isolate and identify the pathogen through microscopic identification at the Forest Health Lab in Fitchburg.
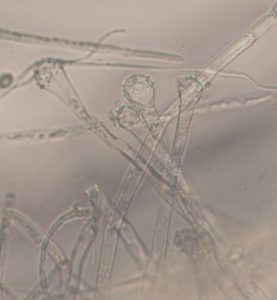
Microscopic spores isolated from wood samples and confirmed as HRD in Forest Health Lab.
Based on this new find, a number of townships were added to the 25-mile buffer zones used in determining appropriate management activities according to the HRD Management Guide. There will be a one-year grace period for implementation of the guide in these townships.
The Forest Health Program has records of all confirmed HRD detections. If you suspect this disease is present in a stand, contact your regional forest health specialist.
For more information about HRD, visit the DNR Forest Health webpage.
