 The cooperative agreement between the USDA Forest Service and the Davey Tree Expert Company, which typically funds the delivery of i-Tree, has been indefinitely halted. Without this funding, maintenance for i-Tree will be impacted and the tools could eventually cease to function.
The cooperative agreement between the USDA Forest Service and the Davey Tree Expert Company, which typically funds the delivery of i-Tree, has been indefinitely halted. Without this funding, maintenance for i-Tree will be impacted and the tools could eventually cease to function.
When Is The Best Time To Prune Trees?
By Elton Rogers, DNR Urban Forestry Coordinator
Elton.Rogers@wisconsin.gov or 414-294-8675
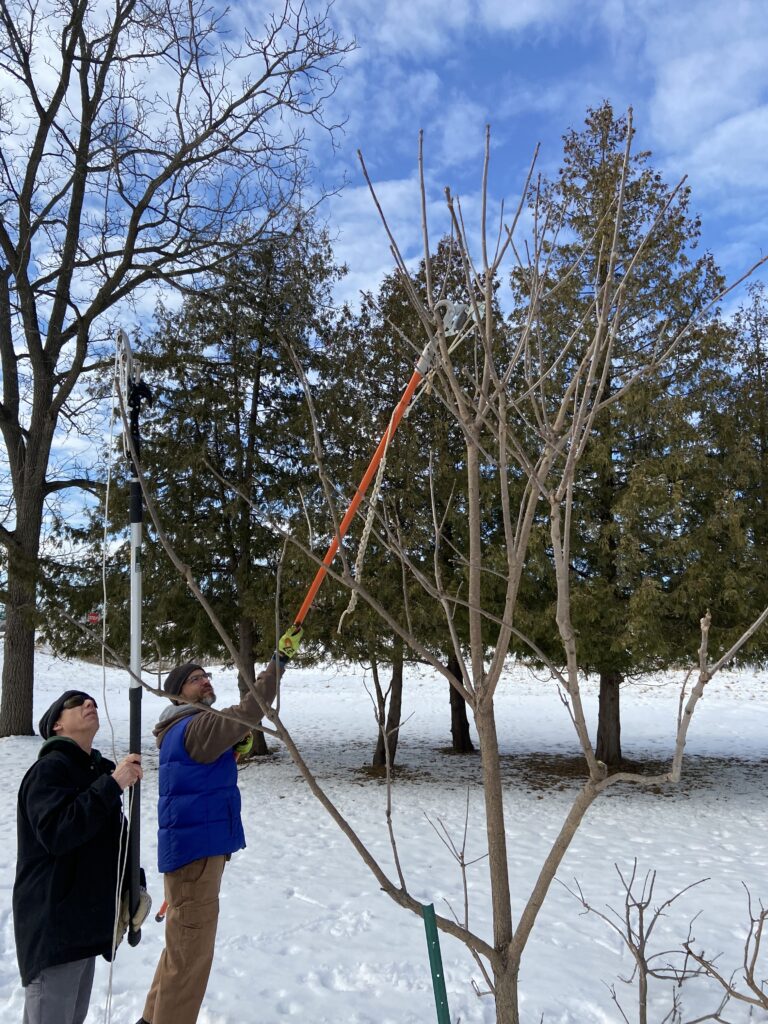 To best answer the titular question, I like to start by flipping the question on its head: When is the worst time to prune trees?
To best answer the titular question, I like to start by flipping the question on its head: When is the worst time to prune trees?
To answer this reworded question, we first need to acknowledge that “pruning is wounding.” Anytime you cut off a living portion of a tree, you are doing two main things:
- Removing photosynthetic material.
- Creating a potential entry point for decay.
A New, Intuitive Way To Measure Species Diversity
By Dan Buckler, DNR Urban Forest Assessment Specialist
Daniel.Buckler@wisconsin.gov or 608-445-4578
Especially in the wake of emerald ash borer, urban foresters have stressed species diversity as an important goal in the management of local trees. Now there is a new, intuitive way of tracking species diversity by simply counting how many species it takes to make up half of your community’s trees.
This metric is called the top diversity index, or TD-50 index, and was proposed in a 2022 article in Urban Forestry and Urban Greening by Natalie Love and others. The index is deceptively simple — by counting the minimum number of species it takes to comprise 50% of your trees, you have an easy benchmark to improve upon to reduce your reliance on a few species. Continue reading “A New, Intuitive Way To Measure Species Diversity”
Application Deadline March 1 For Federal Recreational Trail Program (RTP) Grants
 The deadline to apply for federal Recreational Trail Program (RTP) grants has changed from May 1 to March 1 annually.
The deadline to apply for federal Recreational Trail Program (RTP) grants has changed from May 1 to March 1 annually.
This change is occurring because the RTP grant program guidance and application will no longer be combined with the Knowles-Nelson Stewardship Local Assistance Program and the Federal Land and Water Conservation Fund grant programs.
The goal of the federal RTP is to encourage the maintenance, rehabilitation and development of trails and trail-side amenities by providing cost-sharing assistance to governmental units and qualified trail organizations. Funding is available for both motorized and non-motorized trails. Continue reading “Application Deadline March 1 For Federal Recreational Trail Program (RTP) Grants”
Upcoming Trainings
 * These training opportunities are provided as an information service only and do not constitute an endorsement from the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR).
* These training opportunities are provided as an information service only and do not constitute an endorsement from the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR).
See below for information on training topics and events, including tree diseases and treatments, pest management, landscaping, career advancement, invasive species, pruning, volunteer management, new research, partnerships and developing an urban forest management plan. Continue reading “Upcoming Trainings”
Forest Health Annual Report Hot Off The Presses

The cover of the 2025 Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Forest Health Annual Report. / Graphic Credit: Wisconsin DNR
By Art Kabelowsky, DNR Outreach and Communications, Fitchburg
Arthur.Kabelowsky@wisconsin.gov or 608-335-0167
The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) has made its 2025 Forest Health Annual Report ready to view and download.
This year’s edition contains 55 pages of reporting on forest health issues throughout Wisconsin, detailing methods employed by the DNR and other agencies to control pests, diseases and invasive plants.
Continue reading “Forest Health Annual Report Hot Off The Presses”
Hemlock Borer Attacks Stressed Hemlock
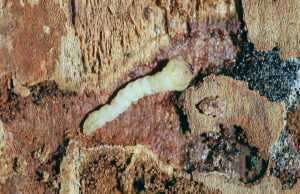
A hemlock borer larva inside channels in a hemlock tree. / Photo Credit: Steven Katovich, Bugwood.org
By Linda Williams, DNR Forest Health Specialist, Woodruff
Linda.Williams@wisconsin.gov or 920-360-0665
Woodpeckers are often the first to know that a hemlock tree is being attacked by hemlock borer.
Woodpeckers will flake off the outer layers of bark to get at the tasty hemlock borer larvae under the bark, leaving the tree with a reddish hue that, once you’ve seen it, is unmistakable. The woodpecker damage quickly makes it obvious that the tree was fully infested from top to bottom by hemlock borer.
Be Mindful Of Invasives During Holiday Clean-Up

A stack of discarded Christmas trees awaits processing at a drop-off facility. / Photo Credit: Wisconsin DNR
By Wisconsin DNR
Invasive plants and insects don’t mind playing the long game. After all, they’re just trying to survive and thrive, like the rest of us.
They’ll hang out as part of your holiday decorations throughout the season, just on the chance humans might dispose of them improperly, giving them an opportunity to find a new home in your yard or neighborhood.
Continue reading “Be Mindful Of Invasives During Holiday Clean-Up”
Invasive Species Action Awards Nominations Open

Winners of the 2025 Invasive Species Action Awards, given by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. / Photo Credit: Wisconsin DNR
By Wisconsin DNR
The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) has announced that the Wisconsin Invasive Species Council will accept nominations for the 22nd annual Invasive Species Action Awards through Feb. 15, 2026.
Award recipients are Wisconsin residents and organizations who have made significant contributions to prevent, control or eradicate invasive species that harm Wisconsin’s native forests, wildlife, wetlands, prairies, lakes and rivers.
Continue reading “Invasive Species Action Awards Nominations Open”
Shively, McNee To Make Public Appearances

Tim Shively, the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Forest Health specialist for the West Central zone. / Photo Credit: Wisconsin DNR
By Art Kabelowsky, DNR Outreach and Communications, Fitchburg
Arthur.Kabelowsky@wisconsin.gov or 608-335-0167
Tim Shively, the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) Forest Health specialist for West Central Wisconsin, will give a presentation titled “Forest Health for Everyone” at a meeting of the Juneau County Men’s Shed at 10 a.m. Tuesday, Jan. 27, in Mauston.
The event is part of a program put on by the Aging and Disability Resource Center of Eagle Country, and will take place at W4890 County Hwy. N, Mauston. It is open to the public. Continue reading “Shively, McNee To Make Public Appearances”
