
The pith of invasive honeysuckle, seen here, is brown and hollow. / Photo Credit: Chris Evans, University of Illinois, Bugwood.org
By Erika Segerson-Mueller, DNR Invasive Plant Program Specialist, Oshkosh;
Erika.SegersonMueller@wisconsin.gov or 715-492-0391
They may have sweet-sounding names, but Eurasian bush honeysuckles (Lonicera spp.) can bring a bitter taste to your mouth if found in your woodlands.
Originating as horticultural plantings, this group of upright woody shrubs is now widespread in Wisconsin and the upper Midwest.
Invasive honeysuckle shrubs are among the earliest plants to leaf out in the spring and the last to lose their leaves in the fall. This extended growing season allows them to outcompete other plants for nutrients and sunlight, casting dense shade on the forest floor.
Native honeysuckles are also present in Wisconsin. Several identifying characteristics can help you determine if your honeysuckle is a native species or one of the invasive varieties. When in bloom, the flowers of invasive Bell’s, Morrow’s and Tartarian honeysuckles are easily distinguished. Without the blooms, the easiest methods to determine non-native honeysuckle from the native plant include looking for shaggy, peeling gray-brown bark and checking the pith.
The pith (inner tissue of the branches and stems) can be observed by breaking off an older branch. If the pith appears white, the shrub is native honeysuckle. If the pith is brown and hollow, it is likely one of the invasive bush versions.
Winter is a great time to treat invasive honeysuckle shrubs on your property since most other plants have gone dormant for the season. Winter herbicide applications are highly successful on freshly cut stumps, provided snow does not cover the cut surface. Basal bark applications may also be used on snow-free surfaces.
Stump cutting should be followed by herbicide treatments, as vigorous resprouting may occur from shrubs cut in winter but not treated with herbicide. Learn more about invasive honeysuckles and how to manage them on the Bush honeysuckles fact sheet from Renz Weed Science at the University of Wisconsin-Extension.
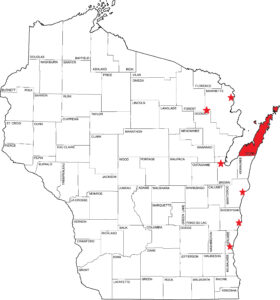




 DNR Urban Forestry welcomes Jenn Janness to the team. She will be focusing on urban forestry outreach and supporting the
DNR Urban Forestry welcomes Jenn Janness to the team. She will be focusing on urban forestry outreach and supporting the 
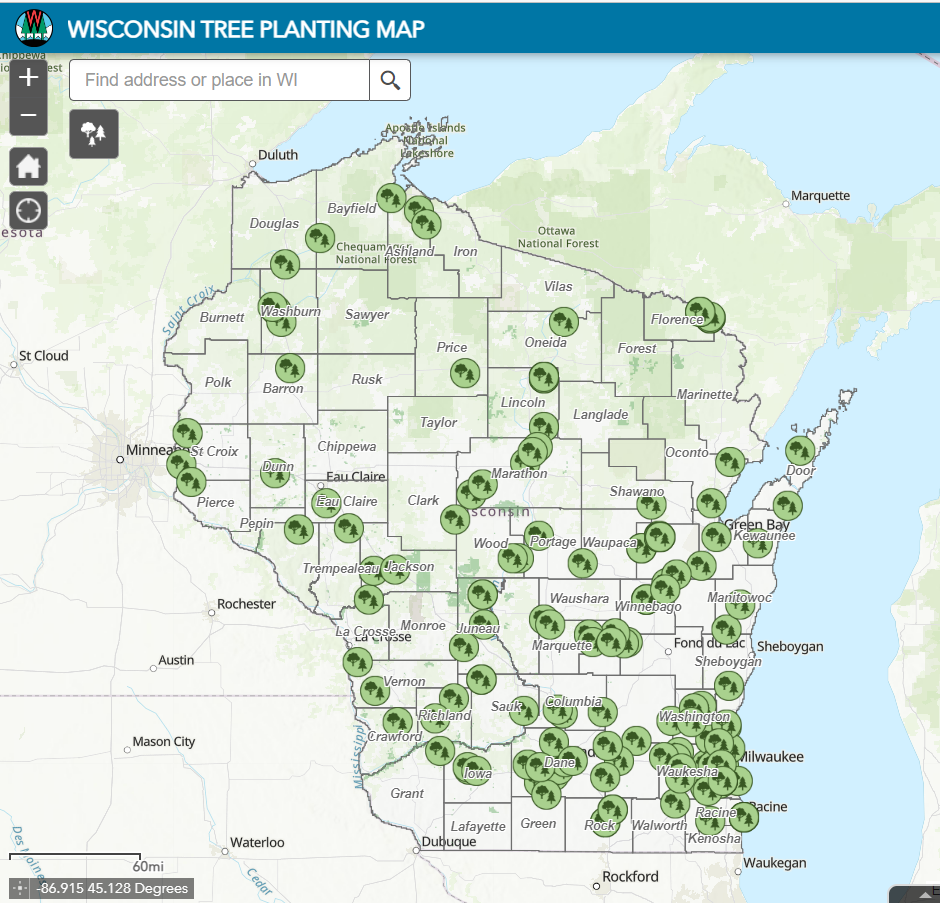 Autumn is a great time to plant trees. After the trees go in the ground, please take a few minutes to document the effort in the
Autumn is a great time to plant trees. After the trees go in the ground, please take a few minutes to document the effort in the