Discolored fallen leaves from a red oak tree indicate that the tree is infected with oak wilt. / Photo Credit: Wisconsin DNR
By Art Kabelowsky, DNR Forest Health Outreach and Communications, Fitchburg Service Center;
Arthur.Kabelowsky@wisconsin.gov or 608-335-0167
With the weather taking its time to turn wintry, it’s a good time to remind landowners and work crews that now through the end of March is an ideal time to perform pruning, trimming and brush removal on and near oak trees.
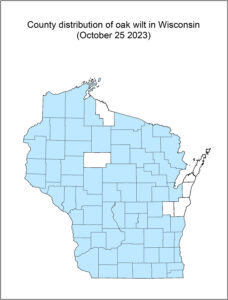
This is a low-risk period for the trees to be infected with oak wilt, a fungal disease spread by beetles. When a red oak is infected with oak wilt, it will die that year. The disease also stresses white oaks, often proving fatal.