The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources has released updated guidelines to reduce the risk of introduction and spread of Heterobasidion root disease (HRD) in Wisconsin through preventive stump treatments. The revised guidelines became effective on January 1, 2019, and a professionally designed version will be available soon. Woodland owners are strongly encouraged to work with a professional forester to make management decisions about HRD and preventive stump treatments.

Pocket of HRD-caused thinning and mortality in red pine plantation, Grant County.
Heterobasidion root disease is one of the most destructive diseases affecting conifers in the Northern Hemisphere. In Wisconsin, HRD is most commonly found in pine and spruce plantations. Infection by the wood-decaying Heterobasidion irregulare fungus kills living tissues and leads to growth loss and tree mortality. Spores landing on a fresh cut pine or spruce stump will infect that stump and root system and spread via root contact to neighboring trees, killing them as it invades their root systems. This pattern of spread creates pockets of dead and dying trees that expand outward. Growth reduction of trees leads to economic losses for plantation owners, and mortality of trees, including seedlings and saplings, has long-term implications for future stand composition and management.
The HRD stump treatment guidelines are designed to help make decisions about the use of preventive stump treatments when harvesting a stand. These treatments limit disease introduction by preventing fungal spores from developing on the exposed surfaces of newly cut stumps.

Pesticides used in stump treatments can be applied using logging equipment (blue mist exiting through nozzles in saw bar) or backpack sprayer.
Stump treatments are typically recommended between April 1 and November 30 if a stand is within 25 miles of a known HRD infection site and the stand is more than 50% pine and/or spruce. However, there are other factors to consider when deciding whether to use the preventive stump treatments. Certain situations when you may not need to treat stumps, referred to as “Exceptions” and “Modifications” in the guidelines, consider variables such as economic feasibility, landowner risk tolerance, unexpected weather patterns and future desired stand composition. Highlights of the revised stump treatment guidelines include:
- Timing of treatments and general distance recommendations did not change from older guidance
- Addition of spruce as a species recommended for stump treatment
- Additional Exceptions and Modifications where treatment may not be necessary
- For private landowners with a higher risk tolerance, a 6-mile radius from known infection sites can be considered when evaluating whether to apply treatments
- Even if a stand is considered at low risk for HRD infection, woodland owners should carefully consider the potential impacts to their stand if preventive treatments are not used and HRD becomes established
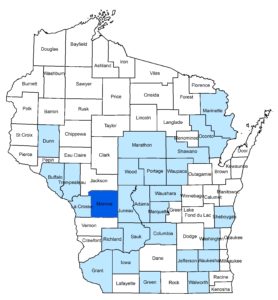
Along with the guidelines, a web-based HRD map viewer has been launched. This interactive map displays confirmed HRD locations and 25-mile and 6-mile radius buffers around HRD locations. The purpose of this map is to help users determine whether a stand is within either the 25 or 6-mile buffers where stump treatments are recommended. You can enter an address or GPS location, turn map layers on and off, and zoom in and out to an area of interest.
If you would like more information about HRD or these guidelines, visit the DNR HRD webpage or talk to your regional forest health specialist.