By Bill McNee, DNR Forest Health Specialist, Oshkosh, bill.mcnee@wisconsin.gov
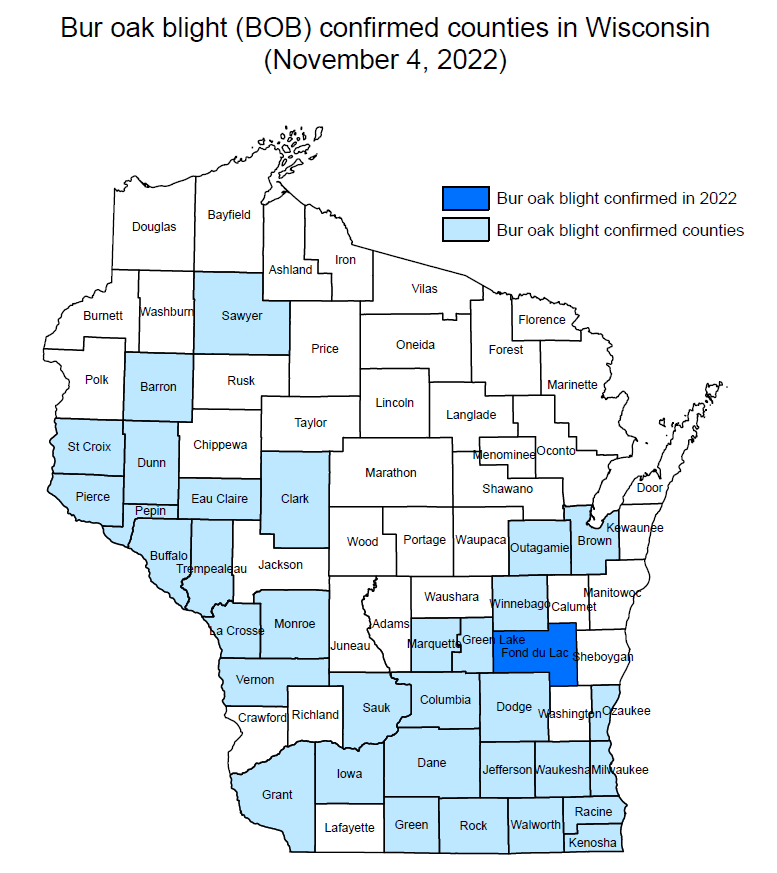
Recent lab examination has confirmed bur oak blight in Fond du Lac County. The disease affects only bur oaks and is caused by the fungus, Tubakia iowensis.
A bur oak on privately-owned land east of Lake Winnebago was reported for a disease believed to be oak wilt, but leaves were visually symptomatic for bur oak blight. Staff from the DNR forest health lab microscopically examined leaf samples from the tree and confirmed that T. iowensis was present.
It is possible for both pathogens (causing bur oak blight and oak wilt) to be present in the same tree, and this has been recently seen in two bur oaks in Winnebago County. However, DNA testing did not find the oak wilt pathogen in branch samples from this Fond du Lac County tree.
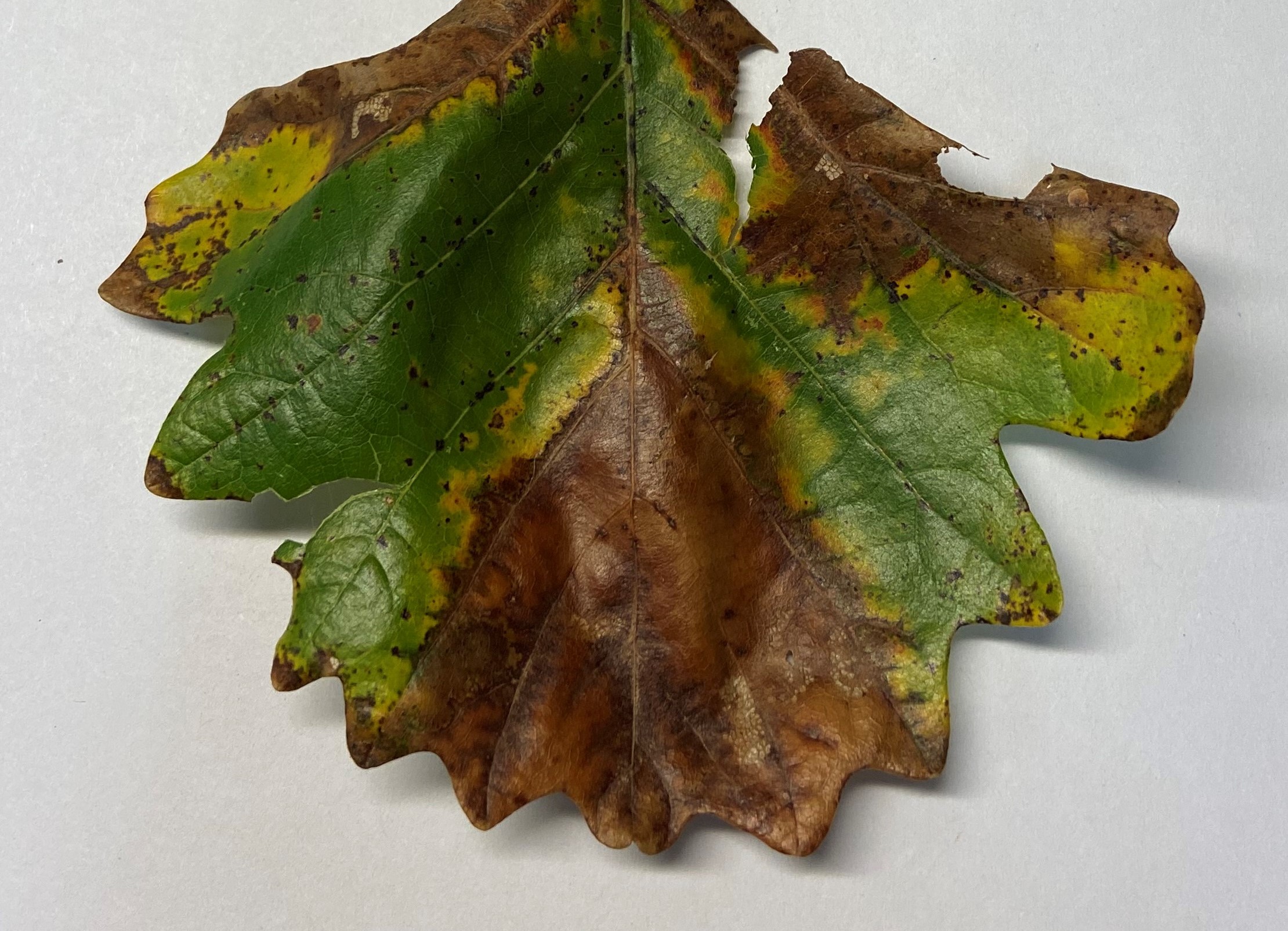

Wedge-shaped area of dead tissue at the tip of a bur oak leaf from the infected tree. Photo: Bill McNee, Wisconsin DNR.
Bur oak blight was first reported in midwestern states in the 1990s. Fond du Lac County is the 34th Wisconsin county to have a confirmed detection of the disease, which is likely present elsewhere but has not been microscopically confirmed in all counties where bur oak grows.
Symptoms of bur oak blight start appearing in late July and August and increase in severity as the season progresses. Late-season symptoms of bur oak blight include a wedge-shaped area of dead tissue on many leaves, and purple-brown lesions on the underside leaf veins. Disease symptoms usually start in lower branches and progress up the canopy during the year. Severely affected bur oaks can lose vigor and may die after many years of infection.
Please report symptomatic trees to your local forest health specialist.