By Paul Cigan, forest health specialist, Hayward, paul.cigan@wisconsin.gov, 715-416-4920
 With the new year upon us, healthy lifestyle habits are sure to be on many people’s minds as they plan for changes in diet and exercise. The new year is also the perfect opportunity to make healthier choices for trees! Winter is the ideal time for tree pruning while avoiding harmful, disease-carrying pests such as the tiny beetles that carry oak wilt from one tree wound to another.
With the new year upon us, healthy lifestyle habits are sure to be on many people’s minds as they plan for changes in diet and exercise. The new year is also the perfect opportunity to make healthier choices for trees! Winter is the ideal time for tree pruning while avoiding harmful, disease-carrying pests such as the tiny beetles that carry oak wilt from one tree wound to another.
“The best time to prune trees that lose their leaves is during winter when the trees are dormant,” said DNR forest health specialist Paul Cigan. “Not only is it easier to see where pruning is needed when leaves are gone, but disease-carrying pests are inactive due to the cold, making pruning both more effective and less likely to invite unwanted pests.”
While pruning in winter reduces the risk of spread through beetles, Cigan pointed out that the disease can spread year-round in firewood. “Several recent oak wilt finds in northern Wisconsin, including a first-ever find in Forest County, may have been the result of infected firewood brought from areas with oak wilt,” Cigan said. “Keep oak firewood where it is cut for one year, or until the bark is naturally loose, to prevent the spread of oak wilt,” he advised.
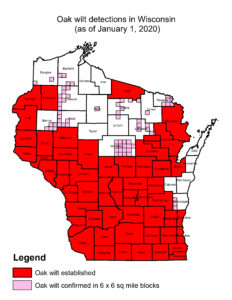
For more information, visit DNR webpages for oak wilt and firewood.
Pruning tips
Yard trees and trees in urban settings should be pruned throughout their entire life to maintain strong structure and remove dead wood. Young trees should be pruned to establish a central trunk, proper trunk taper and good branch structure and spacing. Older trees should be pruned to remove dead and/or hazardous limbs. “Pruning should not remove more than 25 percent of the live tree crown, and the lower third of deciduous tree trunks should be free of limbs,” advised DNR urban forestry coordinator Don Kissinger. You can find more detailed, step-by-step tips for tree pruning in this DNR tree pruning publication.
Certified arborists who offer pruning and other tree care services can be found at waa-isa.org/arborists/search.asp.
 Continue reading “Fighting invasives together through responsible firewood practices”
Continue reading “Fighting invasives together through responsible firewood practices” 
 With the new year upon us, healthy lifestyle habits are sure to be on many people’s minds as they plan for changes in diet and exercise. The new year is also the perfect opportunity to make healthier choices for trees! Winter is the ideal time for tree pruning while avoiding harmful, disease-carrying pests such as the tiny beetles that carry oak wilt from one tree wound to another.
With the new year upon us, healthy lifestyle habits are sure to be on many people’s minds as they plan for changes in diet and exercise. The new year is also the perfect opportunity to make healthier choices for trees! Winter is the ideal time for tree pruning while avoiding harmful, disease-carrying pests such as the tiny beetles that carry oak wilt from one tree wound to another.




