By Jeff Roe, DNR Urban Forestry Team Leader, Madison; Jeffrey.Roe@wisconsin.gov or 608-535-7582
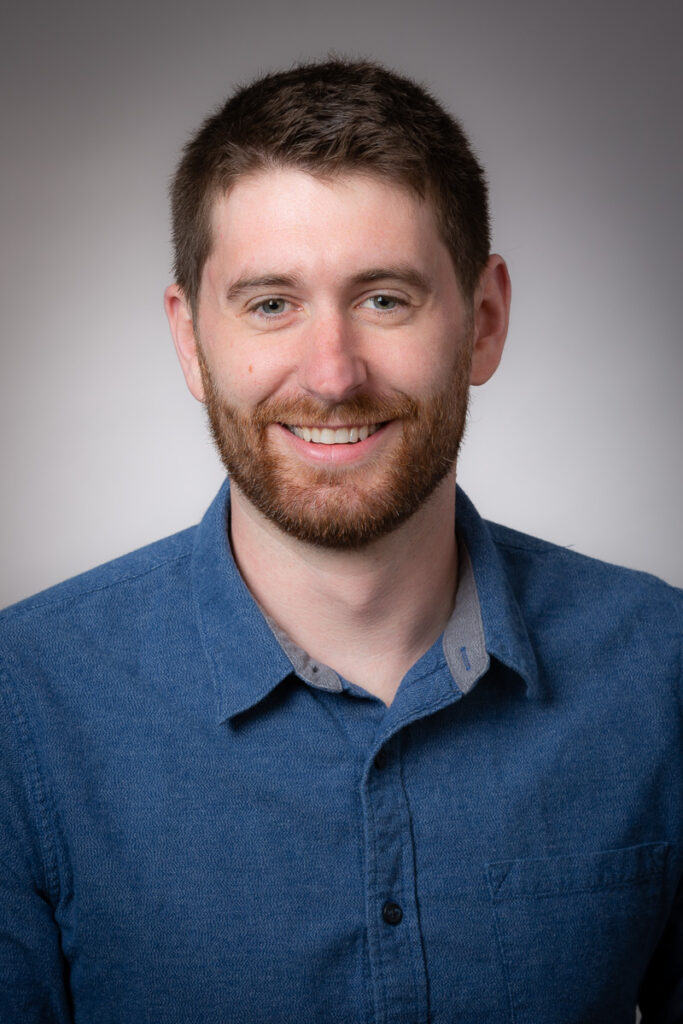 I am pleased to announce that Elton Rogers has accepted the Southeast Regional Urban Forestry Coordinator position. Elton is based in Milwaukee and his first day was Jan. 16.
I am pleased to announce that Elton Rogers has accepted the Southeast Regional Urban Forestry Coordinator position. Elton is based in Milwaukee and his first day was Jan. 16.
Elton holds a bachelor’s degree in geography from the University of Wisconsin Milwaukee and has
earned a graduate certificate in urban forestry from Oregon State University. Additionally, he is
in the final stages of completing his graduate research project to obtain a Master of Natural
Resources degree with an emphasis in urban forestry.
For the past five years, Elton has been a lead faculty member and full-time instructor at Milwaukee
Area Technical College, teaching in both the Landscape Horticulture associate degree program
and the Arborist Apprenticeship program. He is also an ISA Board Certified Master Arborist and
has held various roles in municipal urban forestry programs throughout his professional career.
He is eager to continue collaborating with municipalities, nonprofits and other organizations in
southeastern Wisconsin to help establish and maintain a resilient urban forest.
Outside work, he enjoys exploring local nature preserves with his wife and two kids. A couple of
his hobbies include disc golfing and rope splicing.
You can get a hold of Elton at Elton.Rogers@wisconsin.gov or 414-294-8675.


 Congratulations to Tracy Salisbury, who began her retirement in May. Tracy has been with the DNR as an urban forestry coordinator in northeast Wisconsin since 1998.
Congratulations to Tracy Salisbury, who began her retirement in May. Tracy has been with the DNR as an urban forestry coordinator in northeast Wisconsin since 1998.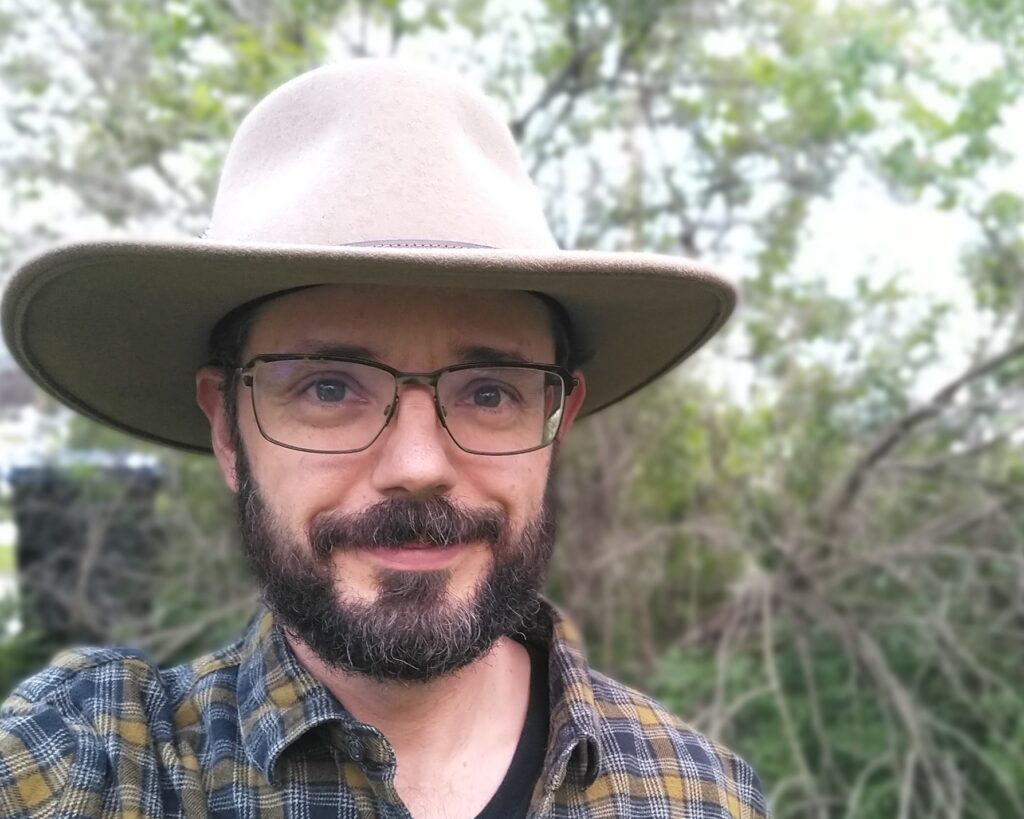 Jay Dampier joined the Urban Forestry Team on June 3 as the new Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) grant coordinator. This is a federally funded project position that will be overseeing $4 million of federally funded grants awarded to Wisconsin communities, tribes and nonprofits. These IRA funds were allocated to the urban forestry program by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Forest Service in 2023. As part of the Justice 40 Initiative, 100% of the funds will be used to improve the urban forest resources and lives of those living in disadvantaged communities throughout the state.
Jay Dampier joined the Urban Forestry Team on June 3 as the new Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) grant coordinator. This is a federally funded project position that will be overseeing $4 million of federally funded grants awarded to Wisconsin communities, tribes and nonprofits. These IRA funds were allocated to the urban forestry program by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Forest Service in 2023. As part of the Justice 40 Initiative, 100% of the funds will be used to improve the urban forest resources and lives of those living in disadvantaged communities throughout the state.  The Wisconsin Forestry Center (WFC) is seeking forestry professionals to create 90-second videos showing an authentic representation of a day in your life as you go about your job duties. The videos will be posted on the WFC’s
The Wisconsin Forestry Center (WFC) is seeking forestry professionals to create 90-second videos showing an authentic representation of a day in your life as you go about your job duties. The videos will be posted on the WFC’s  I am pleased to announce that Elton Rogers has accepted the Southeast Regional Urban Forestry Coordinator position. Elton is based in Milwaukee and his first day was Jan. 16.
I am pleased to announce that Elton Rogers has accepted the Southeast Regional Urban Forestry Coordinator position. Elton is based in Milwaukee and his first day was Jan. 16.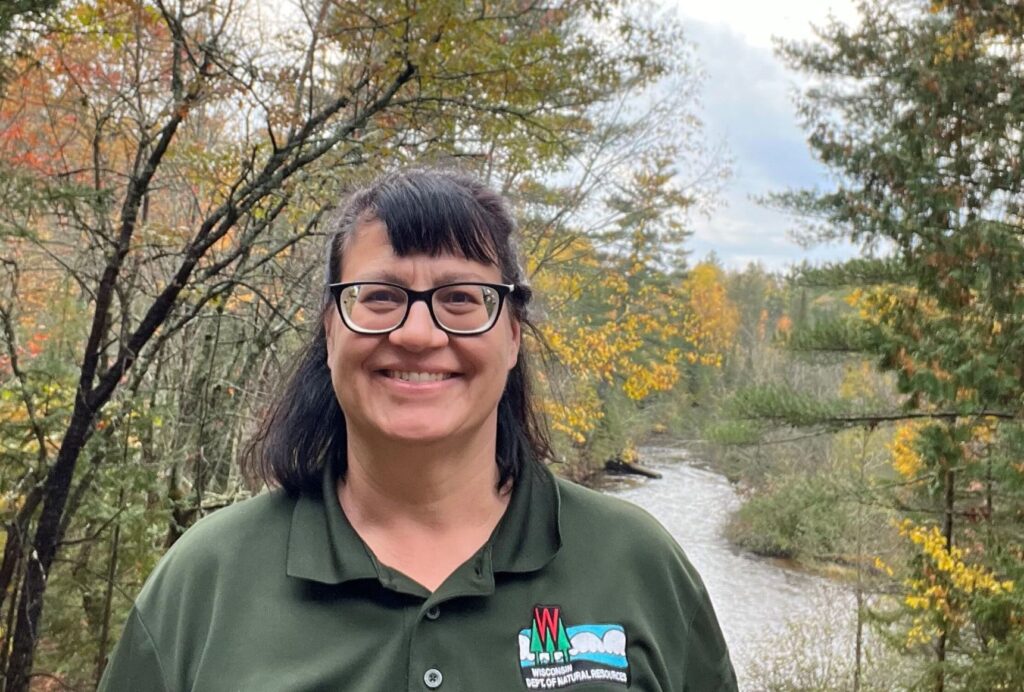 DNR Urban Forestry welcomes Jenn Janness to the team. She will be focusing on urban forestry outreach and supporting the
DNR Urban Forestry welcomes Jenn Janness to the team. She will be focusing on urban forestry outreach and supporting the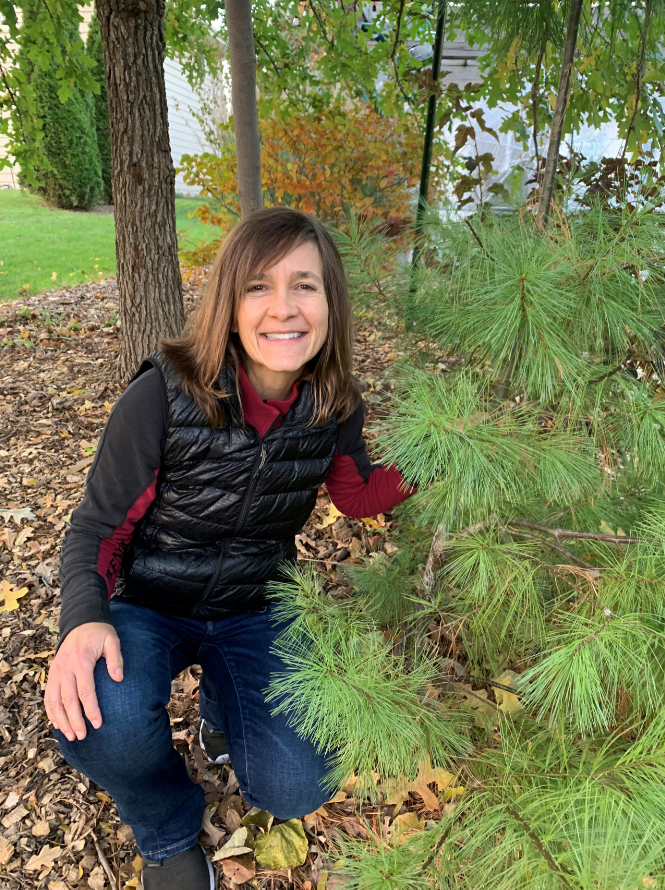  Congratulations to Kim G. Sebastian as she begins her retirement this month. Kim has been with the DNR as Urban Forestry Coordinator since 1990. Read on to hear Kim reflect on her experience with the DNR and share some parting words.
Congratulations to Kim G. Sebastian as she begins her retirement this month. Kim has been with the DNR as Urban Forestry Coordinator since 1990. Read on to hear Kim reflect on her experience with the DNR and share some parting words.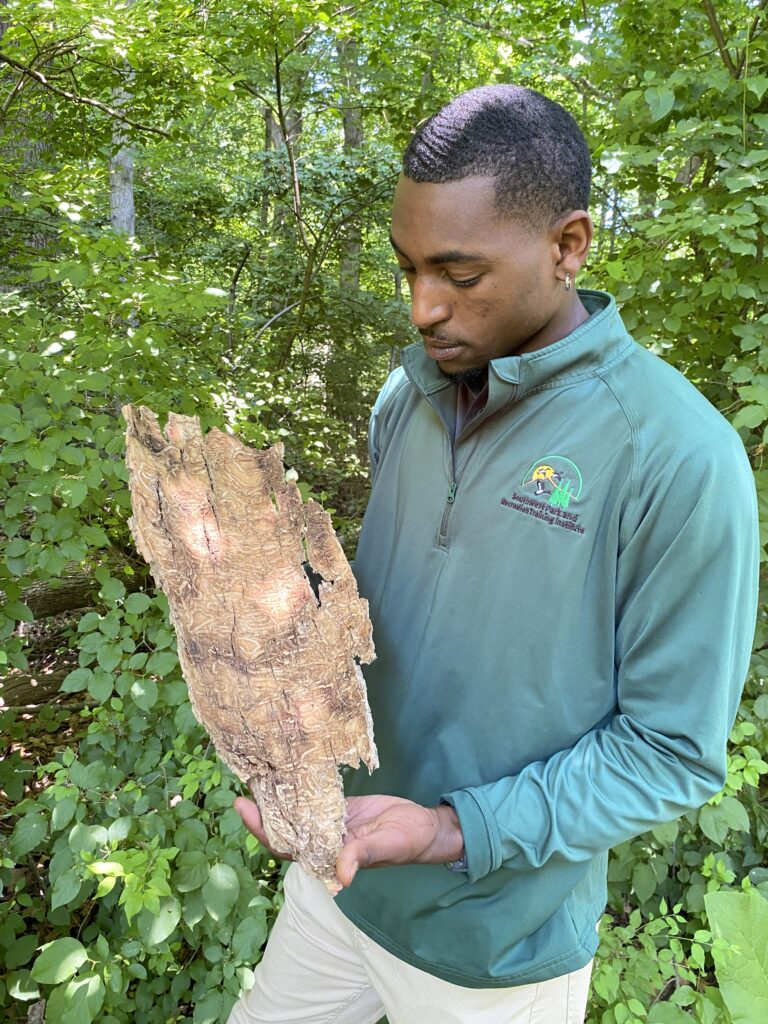 Deron Isom will be graduating this spring from Southern University and A&M College’s Urban Forestry and Natural Resources Department. He chose urban forestry and natural resources to contribute to the care of the environment. During his time at Southern, he had opportunities to intern with the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation and partner with the Recreation & Park Commission for East Baton Rouge Parish to produce multiple resource management plans and tree inventory projects. He is currently employed with the USDA at the Honeybee Breeding, Genetics and Physiology Agricultural Research Lab. He is known for his master status as a professional pugilist as well as pursuing a professional boxing career. He is a member of The Society of American Foresters, The Louisiana Forestry Association, Southwest Parks and Recreation Training Institute, and Spartans Boxing Club. He has goals to increase global contributions to sustainable living and spread his knowledge of agriculture.
Deron Isom will be graduating this spring from Southern University and A&M College’s Urban Forestry and Natural Resources Department. He chose urban forestry and natural resources to contribute to the care of the environment. During his time at Southern, he had opportunities to intern with the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation and partner with the Recreation & Park Commission for East Baton Rouge Parish to produce multiple resource management plans and tree inventory projects. He is currently employed with the USDA at the Honeybee Breeding, Genetics and Physiology Agricultural Research Lab. He is known for his master status as a professional pugilist as well as pursuing a professional boxing career. He is a member of The Society of American Foresters, The Louisiana Forestry Association, Southwest Parks and Recreation Training Institute, and Spartans Boxing Club. He has goals to increase global contributions to sustainable living and spread his knowledge of agriculture.