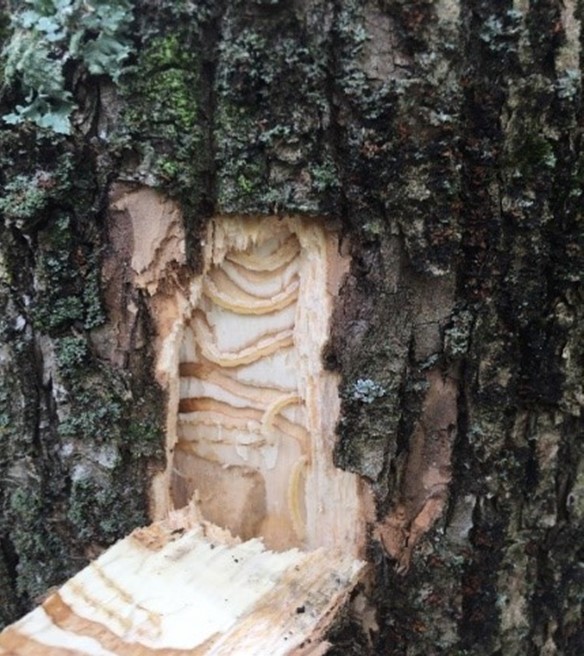
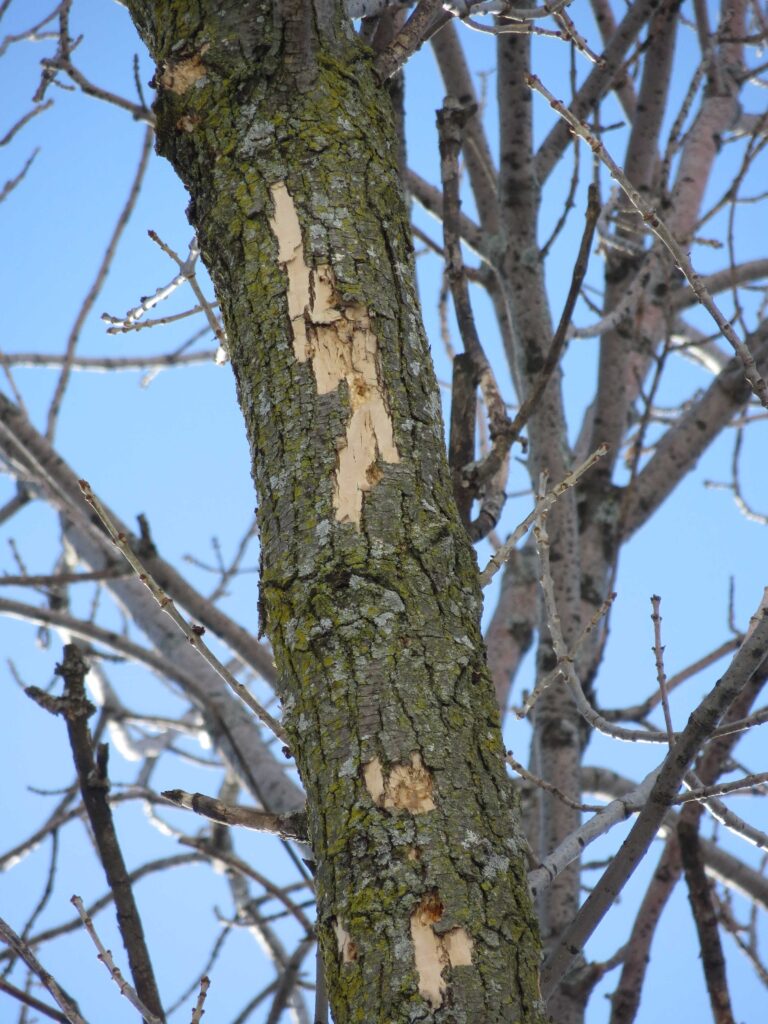
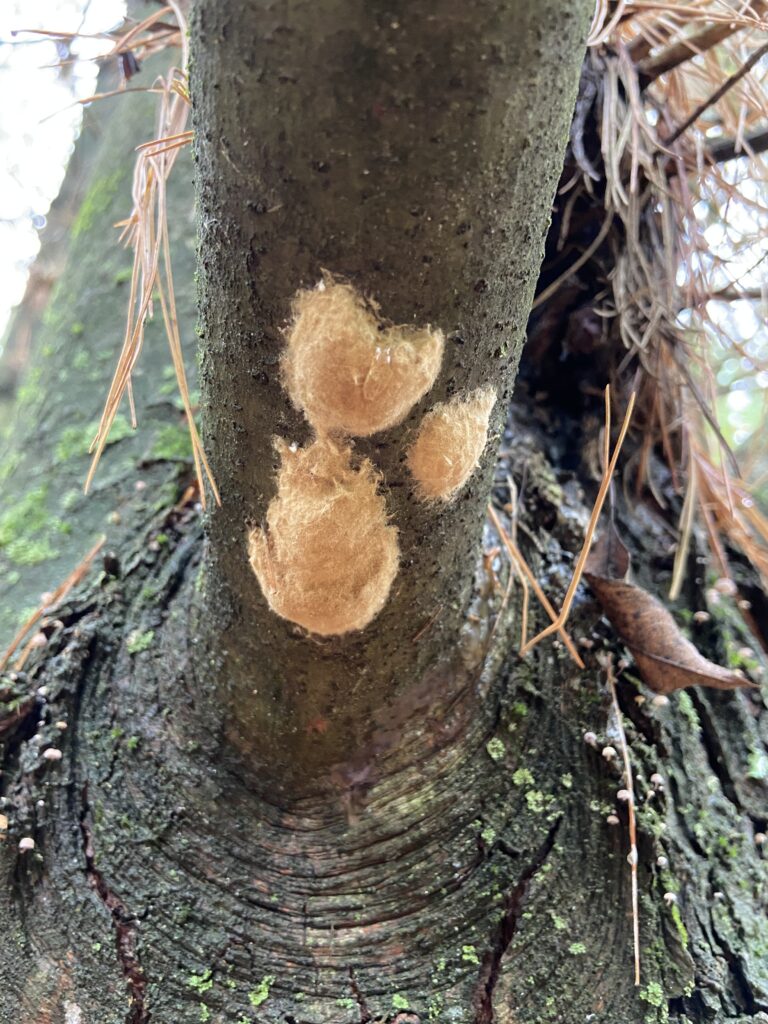
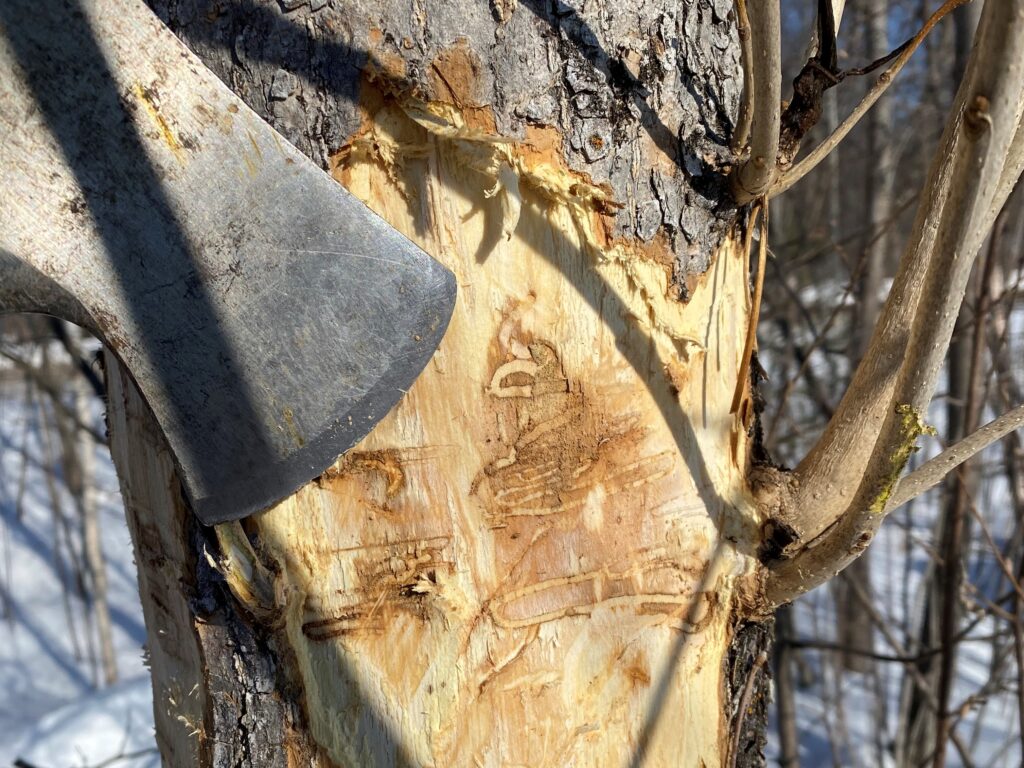
USDA staff cut a ‘bark window’ in green ash to uncover signs of emerald ash borer.
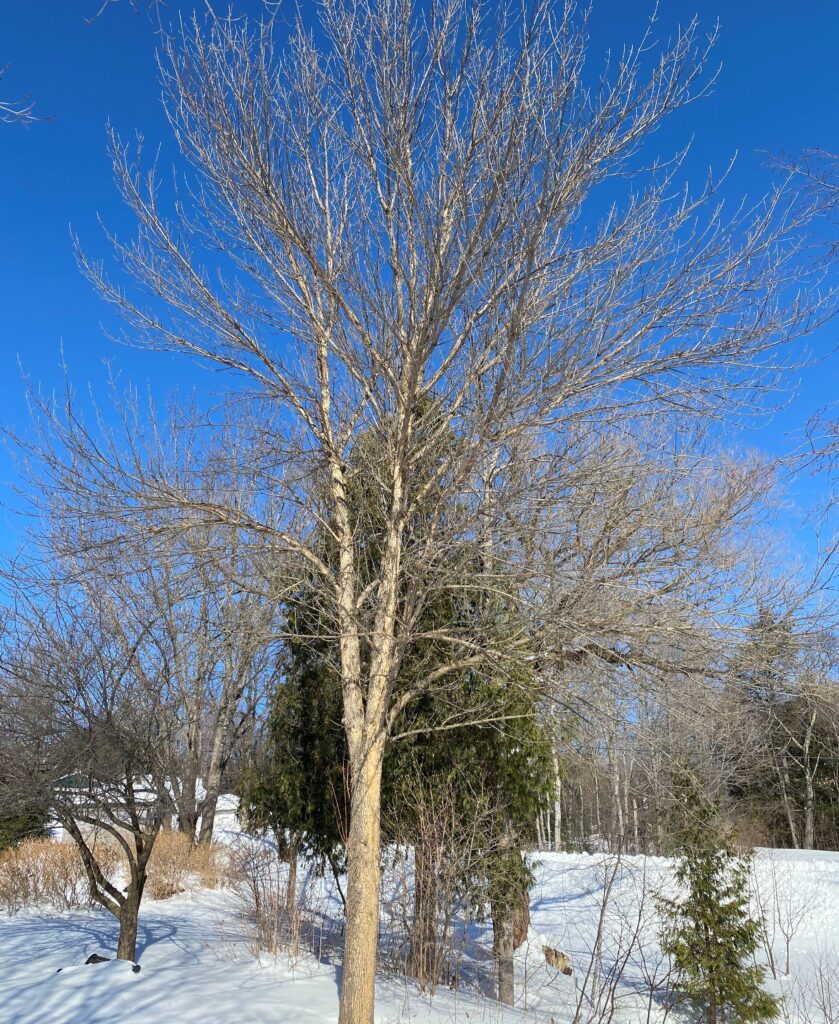
Emerald ash borer (EAB) is an invasive insect from Asia first introduced into the United States in 2002. Since its discovery, EAB has caused tens of millions of ash trees to die and decline. Today, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) uses ash trees against the pest to help preserve and protect the tree species. They are asking Wisconsin landowners for their help.
Wisconsin landowners have donated live, infested ash trees to USDA’s EAB biological control program. The staff will then use the wood to cultivate EAB’s natural enemies and release them in Wisconsin and 28 other EAB-infested states. The biocontrol staff will need more ash trees to continue producing and releasing these stingless wasps that attack and kill EAB and are hoping more Wisconsin residents will consider donating their ash trees this year.
Continue reading “USDA Biological Control Facility Seeks Ash Trees To Battle Emerald Ash Borer”