Art Kabelowsky, DNR Forest Health outreach and communications specialist
Arthur.Kabelowsky@wisconsin.gov or 608-335-0167

The statewide quarantine for emerald ash borer will end July 1, as one of several permanent rule changes proposed by the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection.
Changes are coming to some of Wisconsin’s rules for plant inspection and plant control, following legislative approval of a proposal from the Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP).
The rule changes for ATCP 21 (Clearinghouse Rule CR 22-022), in the works since 2020, will go into effect on July 1.
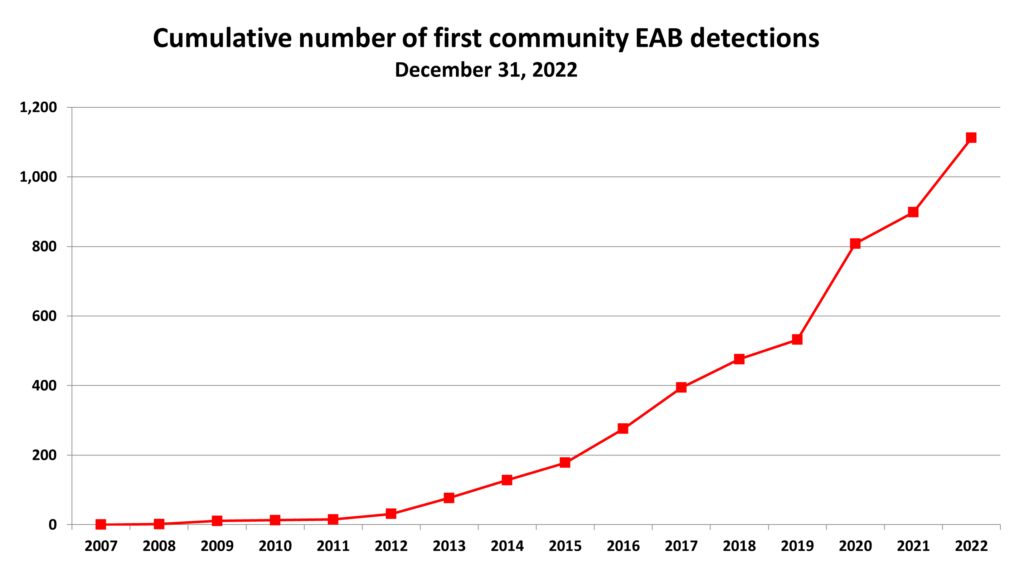
One of the permanent rule changes involves the end of the state quarantine for emerald ash borer. Other quarantines to be rescinded are those for pine shoot beetle and thousand cankers disease of walnut trees.
The changes were recommended by DATCP for one or more of the following reasons: a lack of serious pest impacts, the quarantine outliving its ability to contain the pest, and/or federal deregulation.