
A five-ply panel of Eastern white pine from Wisconsin being formed into cross-laminated timber in a press at Michigan Technological University. / Photo Credit: Wisconsin DNR
By Alex Anderson, DNR Forest Products Specialist, Tomahawk
Alexander.Anderson@wisconsin.gov
As part of the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Forest Products Services mandate to explore new markets for species considered underutilized in the state, a research project was proposed to evaluate the viability of Eastern white pine (EWP) in cross-laminated timber (CLT) panels.
CLT has become increasingly popular in the U.S. during the last decade-plus, after the product was determined to be an effective alternative to traditional concrete and steel construction for multi-story construction in Europe. It is created by pressing dimension lumber (2x4s and 2x6s, typically) into large panels where each layer runs perpendicular to those above or below it, similar to plywood. This construction method allows for large structural panels to be created entirely from wood.
Continue reading “Eastern White Pine CLT Research Moving Along” →
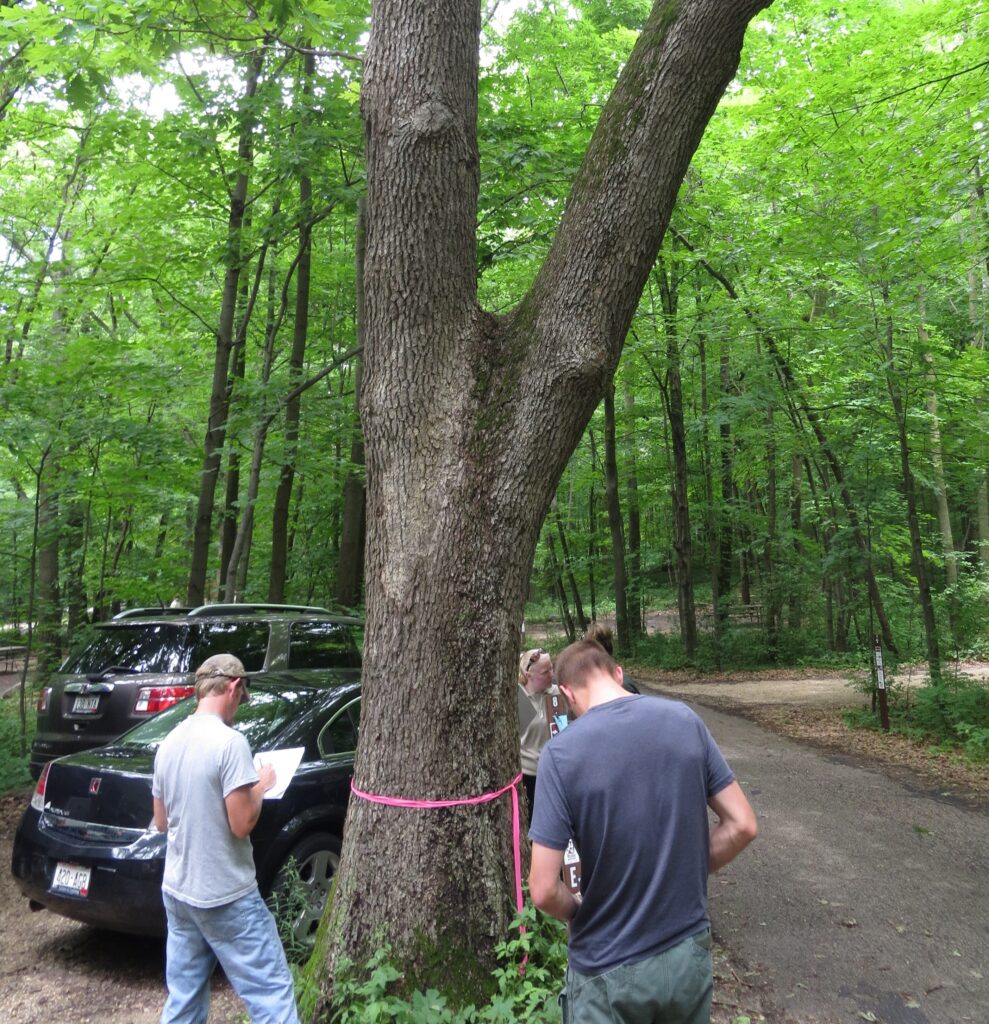 Are you an arborist or urban forester who conducts tree risk assessments?
Are you an arborist or urban forester who conducts tree risk assessments?
 *These training opportunities are provided as an information service only and do not constitute an endorsement from the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR).
*These training opportunities are provided as an information service only and do not constitute an endorsement from the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR).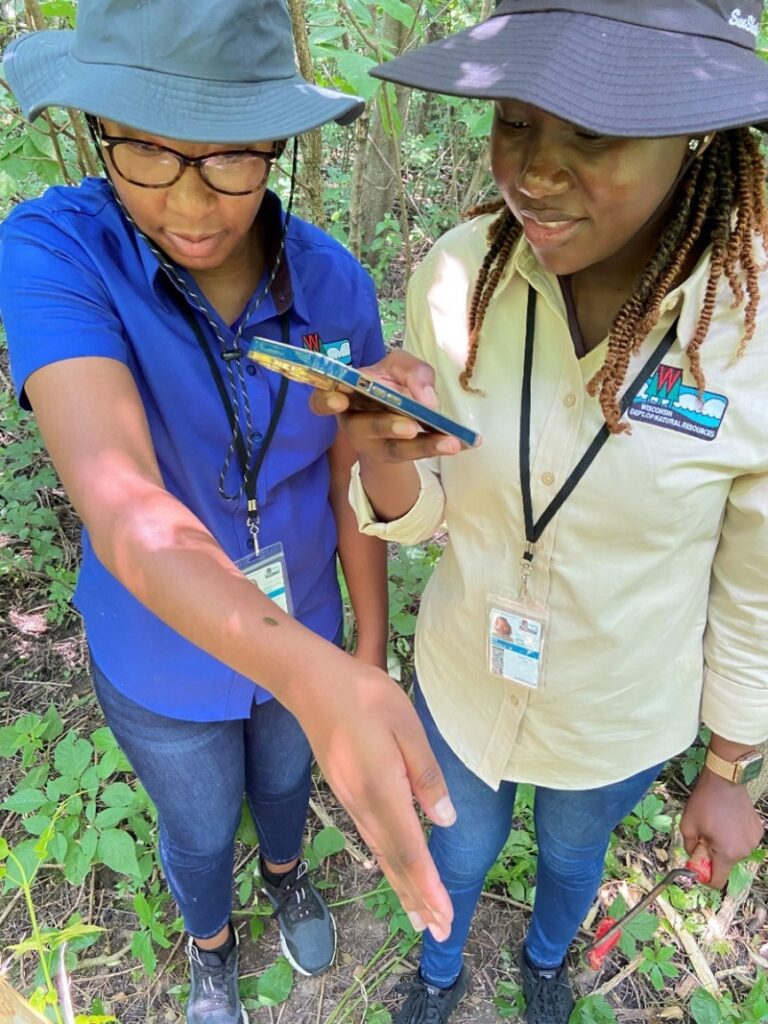 The application period is now open for hundreds of internships with the state of Wisconsin, including two positions with the DNR’s Urban Forestry program!
The application period is now open for hundreds of internships with the state of Wisconsin, including two positions with the DNR’s Urban Forestry program!
 Employee attitudes and well-being improve with exposure to nature. Think about it. Every weekday we commute to work, only to be met by a dark cubicle in shades of beige and grey. Ever wonder why your mood starts to match the walls? It’s because the workplace environment contributes to employee health. We’ve known this to be true (anecdotally) for a long time, but mounting scientific evidence proves our urban and community forests have beneficial effects on employee performance.
Employee attitudes and well-being improve with exposure to nature. Think about it. Every weekday we commute to work, only to be met by a dark cubicle in shades of beige and grey. Ever wonder why your mood starts to match the walls? It’s because the workplace environment contributes to employee health. We’ve known this to be true (anecdotally) for a long time, but mounting scientific evidence proves our urban and community forests have beneficial effects on employee performance.