Article By: Bill McNee, DNR Forest Health Specialist, Oshkosh
bill.mcnee@wisconsin.gov or 920-360-0942
In 2021, gypsy moth populations increased for a second consecutive summer due to favorable weather conditions. Populations typically increase with an average or mild winter, below average spring precipitation and above average May through June temperatures.
Regional variation in weather can result in significant differences in populations. If weather conditions are favorable again in 2022, the most noticeable increase in caterpillar numbers would likely occur in southern counties, where conditions were driest during this past spring and summer.
Populations experience the fastest growth rate and are first noticed on:
- Dry sites with sandy soil and abundant oak
- Mowed lawns with preferred tree species (oak, crabapple, birch, etc.)
- Large oaks (bur, in particular) with rough bark, especially on or adjacent to mowed lawns
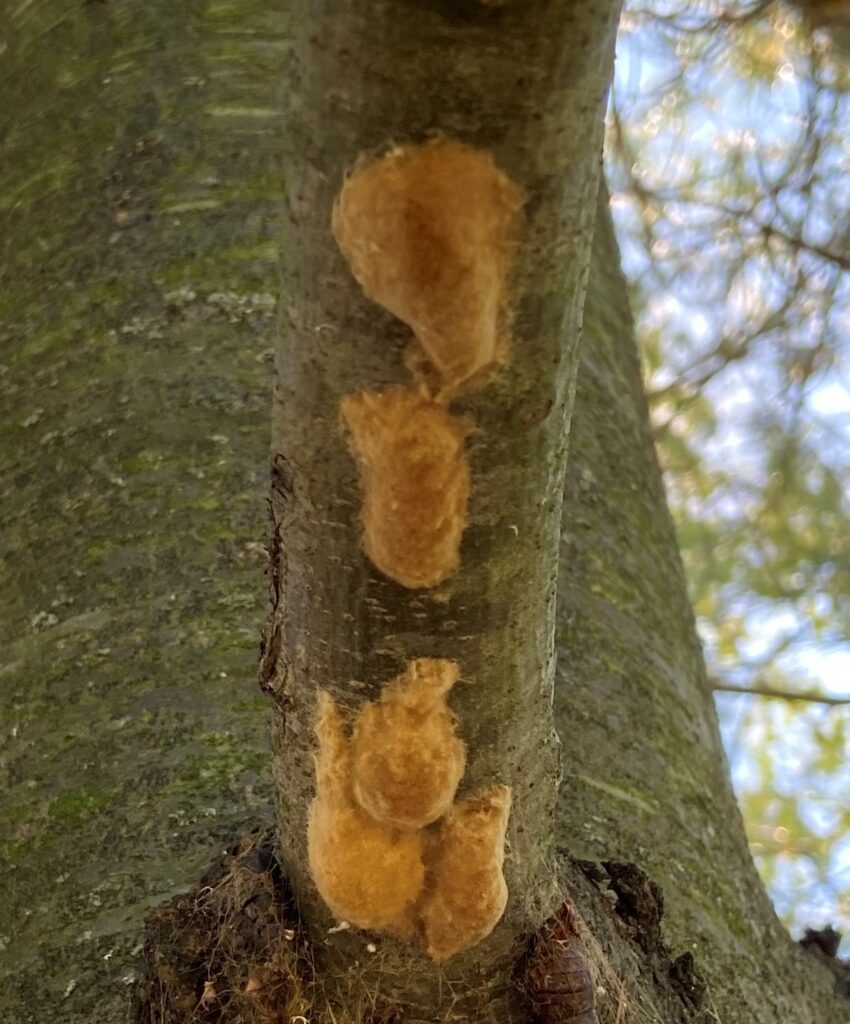

Gypsy moth egg masses found in Walworth County in fall 2021.
Photo Credit: Gypsy moth egg masses KMSU
Continue reading “Take Action! Look For Gypsy Moth Egg Masses”

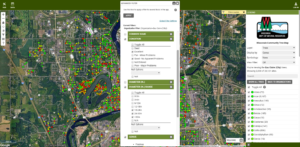
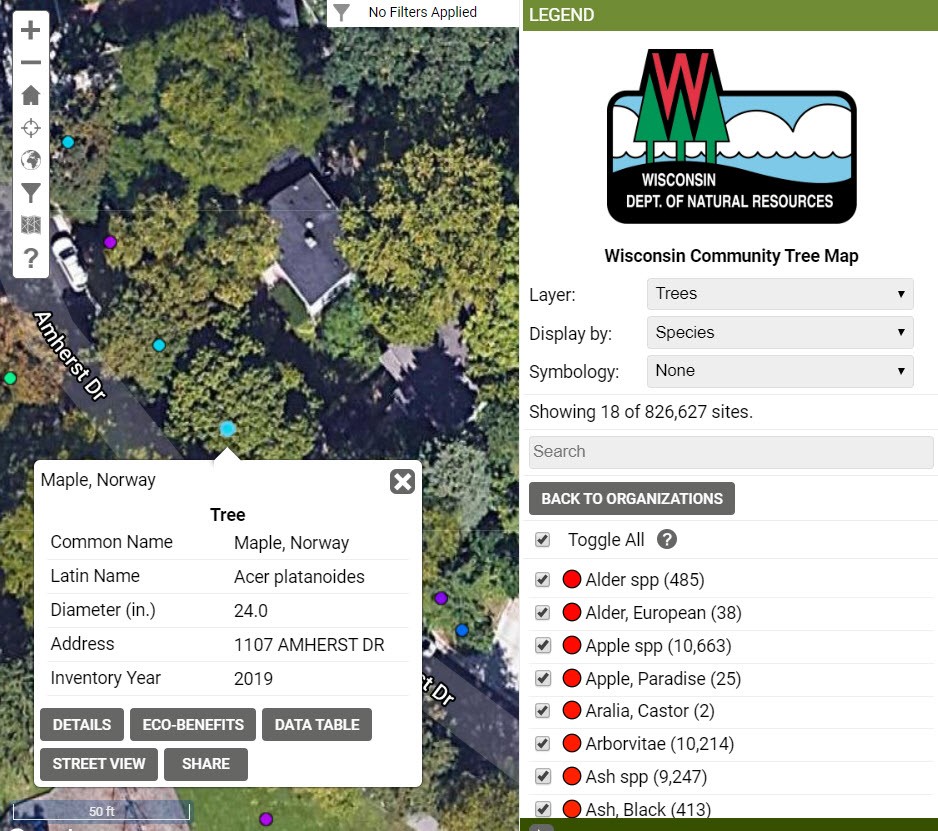 Do you have a tree inventory but have had a hard time keeping it current, or you’re interested in inventorying some trees of your own? The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) is funding several accounts for communities or organizations to edit data within the
Do you have a tree inventory but have had a hard time keeping it current, or you’re interested in inventorying some trees of your own? The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (DNR) is funding several accounts for communities or organizations to edit data within the 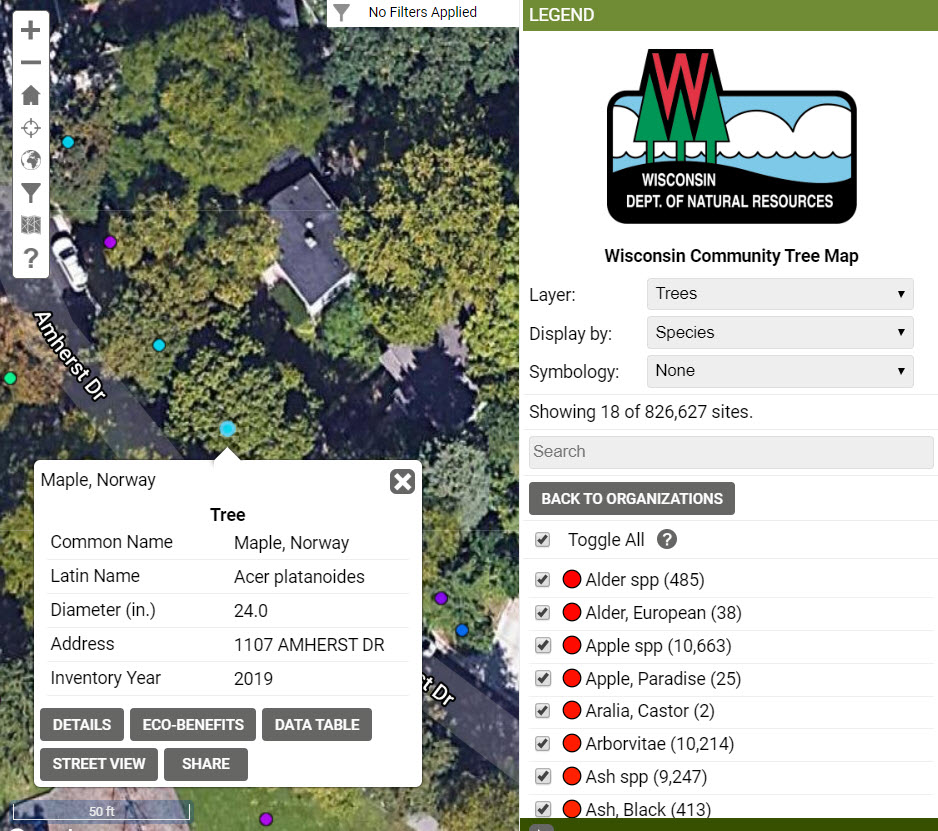
 Wisconsin’s urban forests provide a wide range of ecological, economic and social benefits. Urban areas contain nearly 27 million trees with an estimated total replacement value of almost $11 billion. Many don’t realize all the services urban forests provide. They reduce air pollution, mitigate storm water runoff, conserve energy, provide wildlife habitat, increase property values, and attract businesses, tourists and residents. They even improve public health and well-being. The Wisconsin DNR’s Urban Forestry Team seeks to maximize these benefits derived from our state’s community tree canopies.
Wisconsin’s urban forests provide a wide range of ecological, economic and social benefits. Urban areas contain nearly 27 million trees with an estimated total replacement value of almost $11 billion. Many don’t realize all the services urban forests provide. They reduce air pollution, mitigate storm water runoff, conserve energy, provide wildlife habitat, increase property values, and attract businesses, tourists and residents. They even improve public health and well-being. The Wisconsin DNR’s Urban Forestry Team seeks to maximize these benefits derived from our state’s community tree canopies.  After much deliberation, WI DNR Urban Forestry has decided to postpone the Community Tree Management Institute (CTMI) for one year. The health and safety of others is paramount. Due to the pandemic, it’s just not feasible to come together in person for this training. Group interaction and networking are an integral part of the CTMI experience, so we will look forward to coming together in the fall of 2021 with the start of the next CTMI class (exact dates to be determined).
After much deliberation, WI DNR Urban Forestry has decided to postpone the Community Tree Management Institute (CTMI) for one year. The health and safety of others is paramount. Due to the pandemic, it’s just not feasible to come together in person for this training. Group interaction and networking are an integral part of the CTMI experience, so we will look forward to coming together in the fall of 2021 with the start of the next CTMI class (exact dates to be determined). 
 With thousands of trees on their properties, municipalities and other urban ownerships sometimes need to remove a large volume of trees at once, such as after an insect or disease outbreak (i.e., emerald ash borer) or a catastrophic weather event (wind/tornadoes or ice/snow damage). When this need arises, what are the options available to remove these trees efficiently, safely, cost effectively and quickly?
With thousands of trees on their properties, municipalities and other urban ownerships sometimes need to remove a large volume of trees at once, such as after an insect or disease outbreak (i.e., emerald ash borer) or a catastrophic weather event (wind/tornadoes or ice/snow damage). When this need arises, what are the options available to remove these trees efficiently, safely, cost effectively and quickly?