 By Jodie Ellis, communications specialist, Madison. Jodie.Ellis@wisconsin.gov; 608-843-3506
By Jodie Ellis, communications specialist, Madison. Jodie.Ellis@wisconsin.gov; 608-843-3506
Thanks to all of you who participated in our recent reader survey. About one-fifth of subscribers (336 out of 1,741) took part, providing valuable information which will help us develop better ways to serve all of our readers. The survey was completed April 15, 2018.
Following are some of the things we learned.
Numbers are rounded to the nearest whole number. Some participants chose to skip some questions. Questions are presented below with the total number of respondents indicated in parentheses.
- Do you live in Wisconsin (336)? Yes – 93% No – 8%
- Do you work in Wisconsin (335) Yes – 87% No – 13%
- Do you own forested land in Wisconsin? (336) Yes – 54% No – 46%
- How many acres of forested land in Wisconsin do you own? (180)
Less than 5 acres 13%
5 – 10 acres 14%
11 – 100 acres 54%
More than 100 acres 19%
- Where do you own forested land in Wisconsin? (179)
Northeast zone 30%
East central zone 18%
Northwest zone 18%
West central zone 5%
Central zone 21%
South central zone 12%
Southeast zone 4% MAP
- I am most interested in articles concerning the following zones (refer to older map) (319).
Northeast zone 26%
East central zone 15%
Northwest zone 19%
West central zone 10%
Central zone 21%
South central zone 11%
Southeast zone 10%
Not interested 1%
How often do you read Forest Health News? (318)
Each time I receive an e-mail notification 74%
More than half the time 20%
Less than half the time 4%
Seldom or never 1%
How would you rate the overall content of Forest Health News? (319)
Excellent 43%
Good 52%
Neither good nor poor 5%
Poor n/a
Terrible n/a
- How often do you find information that you can use in your work? (317)
Always 22%
Usually 44%
Sometimes 28%
Seldom 5%
Never 1%
- In general, how interesting or not interesting are topic in Forest Health News to you? (318)
Very interesting 31%
Mostly interesting 62%
Neither interesting or uninteresting 6%
Mostly uninteresting 1%
Very uninteresting < 1%
- Are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the timeliness of the information in Forest Health News? (318)
Extremely satisfied 30%
Usually satisfied 58%
Neither satisfied or dissatisfied 11%
Usually dissatisfied n/a
Extremely dissatisfied n/a
- Do you agree or disagree that Forest Health News is useful to you? (318)
Completely agree 71%
Somewhat agree 25%
Neither agree nor disagree 3%
Somewhat disagree 1%
Completely disagree n/a
- What types of articles do you usually read in Forest Health News? (318)
I read all articles. 33%
I read only articles specific to my zone(s). 12%
I read only articles designated as statewide. n/a
I read a mix of articles, from both the statewide category and articles in specific zones categories. 55%
- Is it currently easy or difficult to move from article to article online? (316)
Easy 65%
Neither easy nor difficult 28%
Difficult 7%
- Please indicate how each of the four categories below is relevant to your work.
| Category |
Extremely relevant |
Mostly relevant |
Neither relevant nor irrelevant |
Mostly irrelevant |
Extremely irrelevant |
| Information about quarantines and other regulatory concerns (314)
|
46% |
32% |
14% |
5% |
3% |
| Current pest and disease observations and management information (313) |
59% |
30% |
6% |
3% |
2% |
| General education information about invasive plants and pests (313)
|
49% |
38% |
8% |
3% |
2% |
| Management and regulation of invasive species (312)
|
49% |
36% |
10% |
4% |
2% |
- From the list of four categories above, which is the most important to your work or interests? (314)
Information about quarantines and other regulatory concerns 12%
Current pest and disease observations and management information 60%
General educational information about invasive plants and pests 15%
Management and regulation of invasive plants 13%
- How often would you like to receive Forest Health News? (317)
Once a month all year round. 38%
Once every two months all year round. 19%
Monthly during the growing season; less frequently during winter. 19%
The frequency is not important to me. 24%
- What is your age? (317)
Under 20 years old n/a
20-25 years old 3%
26-35 years old 14%
36-45 years old 19%
46-55 years old 25%
Older than 55 years 40%
- How would you rate the speed of internet service in your area? (316)
Fast 39%
Adequate 48%
Slow 13%
- Which category best describes you? (318)
Forester 48%
Land manager 7%
Logger < 1%
Mill employee n/a
Craftsman < 1%
Scientist/researcher 3%
Student < 1%
Policymaker < 1%
Education/outreach professional 4%
Professional/business services 7%
Landowner 19%
Other 11%
- If you are reading Forest Health News for information pertaining to your job, who is your employer? (268)
Federal agency 3%
State agency 49%
County agency 8%
Municipal agency 7%
Private sector 16%
Tribal government or business 1%
Non-profit organization 2%
Academic institution 2%
Other 13%
- What federal agency do you work for? (9)
USDA n/a
APHIS n/a
US Forest Service 44%
Other 56% (none specified)
- Which state agency do you work for? (133)
WI DNR 92%
WI DATCP <1%
Other 7%
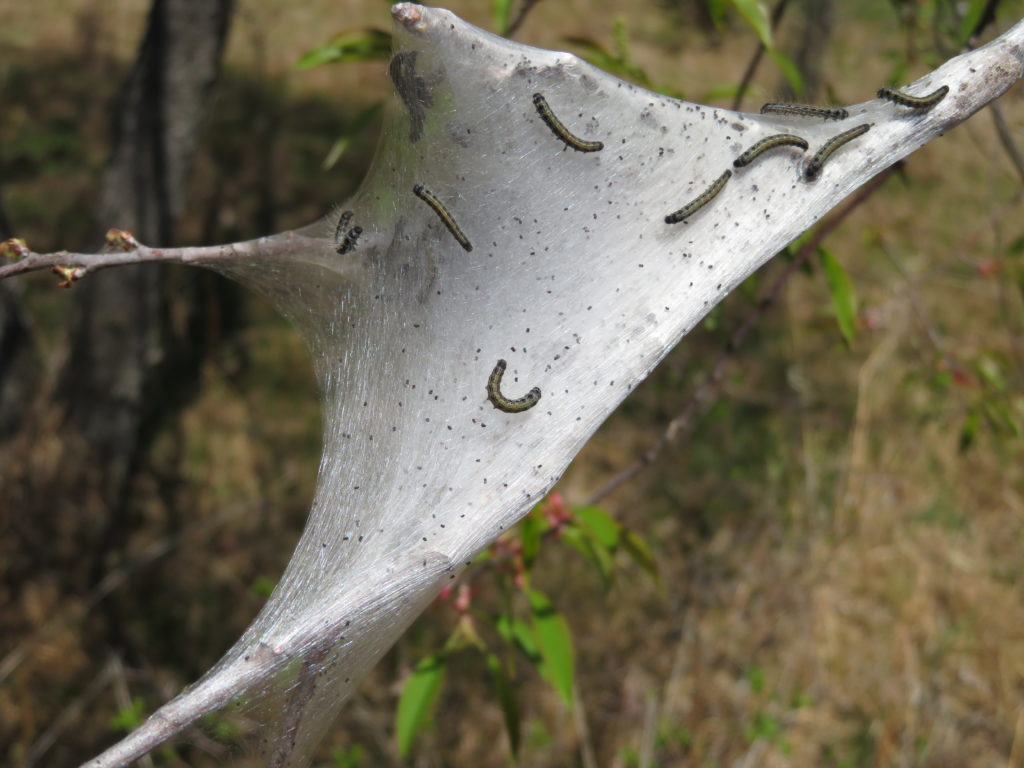
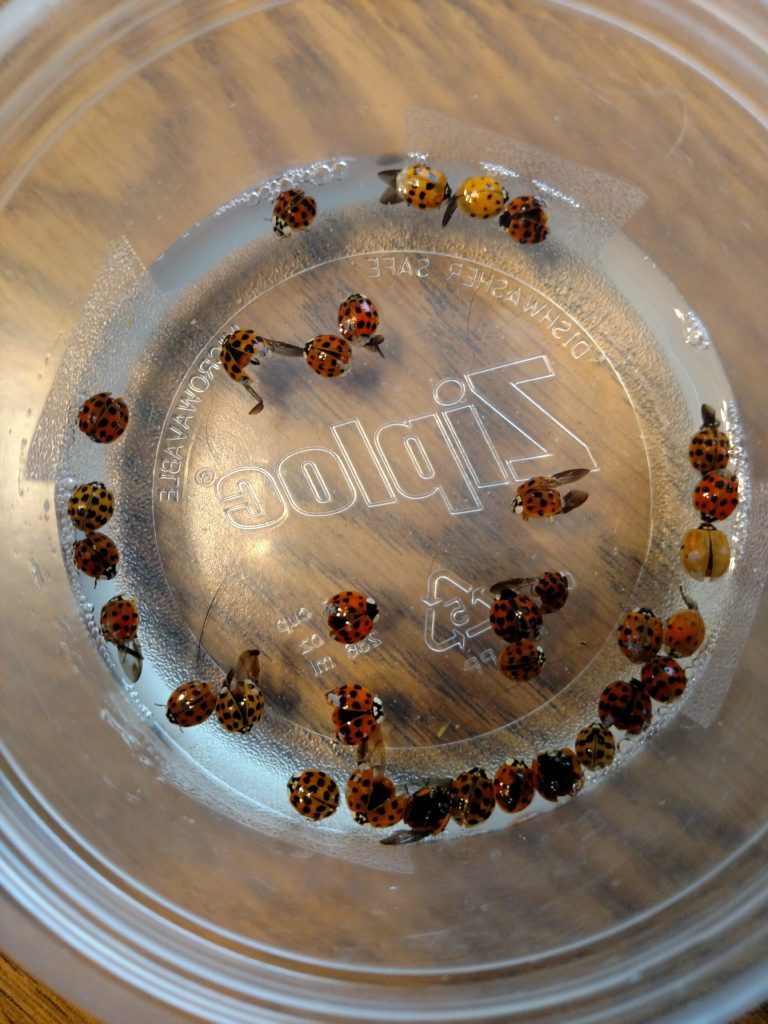






 By Jodie Ellis, communications specialist, Madison. Jodie.Ellis@wisconsin.gov; 608-843-3506
By Jodie Ellis, communications specialist, Madison. Jodie.Ellis@wisconsin.gov; 608-843-3506

